tibial torsion test infant|how to measure tibial torsion : Brand Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of . Download Windows Live Messenger. An instant message program for Windows users. Virus Free
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da LisNet - INTERMÉDICA. Paciente. Ok. Solicitação. Senha. 2012 - 2024 - INTERMÉDICA - Todos os direitos reservados - Lisnet by z6 v14.72 - 147/23.
tibial torsion special test
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance.
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A physical exam can diagnose tibial torsion. .
tear lab osmolarity test
The diagnosis of tibial torsion is made by a history and physical examination by your child's doctor. During the examination, the doctor obtains a complete prenatal and birth history of the .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A .Internal tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the tibia, which leads to in-toeing of the foot. Although it may not be noticeable until your child starts to walk, this condition is often present .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. A .
Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the .Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with .
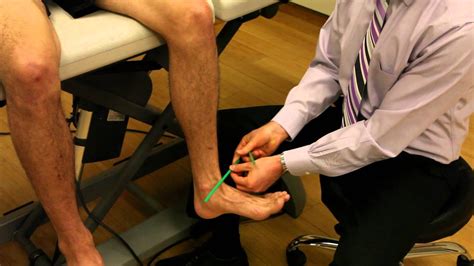
Persistent, excessive internal torsion can lead to toe-ing in (pigeon toes) and bowlegs. Doctors can detect this birth defect by doing a physical examination and taking various measurements .Special Test: Tibial Torsion Test PROCEDURE (Seated): tibial torsion is measured by having the patient sit with the knees flexed to 90° over the edge of the examining table. the examiner places the thumb of one hand over the apex of one malleolus and the index finger of the same hand over the apex of the other malleolus.
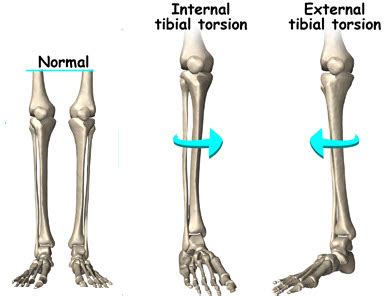
Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, and about two thirds of patients are affected bilaterally. [1, 2] Tibial torsion can persist into adulthood and give rise to patellofemoral pathology. External tibial torsion is usually seen between four to seven years of age. 1, 9 It is often unilateral and more common on the right side. 9 The tibia rotates laterally with growth, making lateral .Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. The child may look pigeon-toed. It is typically seen among toddlers. Causes. Tibial torsion can happen because of the position of the baby in the uterus. It also tends to run in .
knee pain when associated with tibial torsion. . trochanteric prominence angle test . . look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- mean 5° internal (range, −30° to +20°) normal value at age 8 years- mean 10° external (range, −5° to +30°) metatarsus adductus.Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child's feet to turn inward. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for .
Create Group Test Enter Test Code . Metatarsus Adductus is a common congenital condition in infants that is thought to be caused by intra-uterine positioning that lead to abnormal adduction of the forefoot at the tarsometatarsal joint. . > 10° of internal rotation is indicative of tibial torsion (normal is 0-20° of external rotation .
Rigid Forefoot Valgus - This foot prematurely converts to propulsion at a time when it should still be absorbing shock. Symptoms include a tendency to ankle sprains, an unsure gait, every foot pain imaginable, leg muscle problems, stress fractures, etc. Orthotic treatment includes an orthotic that tricks the forefoot into thinking all the bones are level with each other by bringing .
Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equilibri.Some children with tibial torsion wear a night brace between 18 to 30 months old, but this is not common. . A diagnostic test that produces images of internal tissues, . ankles, knees, legs, and hips. Whether the patient is an infant, child, or adolescent, our goal is to help children live full, independent lives. Walking (Gait .Anne Frank Test pt.2 (packet questions) 34 terms. hicksmel000. Preview. contemporary healthcare vocab. 9 terms. . Which of the following is the most reliable assessment method to assess for developmental dysplasia of the hip in an infant? a) Allis test b) Gluteal fold comparison c) Tibial torsion d) Ortolani maneuver. d) Ortolani maneuver.Paediatric lower extremity and gait concerns are common reasons for visits to paediatricians and therapy services.[1][2][3][4][5] They can account for up to 16% of all new paediatric orthopaedic surgeon referrals.[6] Parents commonly worry about in- or out-toeing or that their child might be delayed in meeting developmental milestones because of lower extremity or gait .
Internal tibial torsion is most frequently bilateral, and may at times present with metatarsus adductus, femoral anteversion, or physiologic bow legging. Pertinent clinical findings on examination include a forward or outward-facing patella, or in a seated position, there may be a posterior rotation of the medial malleolus (in comparison to the . Create Personal Test Create Group Test Enter Test Code Active Test Cases. Cases. Cases . apparent genu valgum with excessive femoral anteversion or external tibial torsion . general exam to assess stigmata of .Internal Tibial Torsion . In-toe walking can often be caused by an inward twist of the tibia (shin bone). This is very common in babies and toddlers and is due to 'moulding' of the baby during pregnancy. It may persist for a few years but gradually disappears as the child grows. Treatment with splints, plasters or braces does not alter it and .
Pediatric tibial torsion happens when a child is born with the tibia (shin) bone slightly twisted or rotated, which causes the foot to turn inward. This common condition causes intoeing, which means the toes turn inward, which is especially noticeable when the child walks. What are the signs and symptoms of tibial torsion in children? Symptoms .Tibial Torsion in Children What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean.
Dr. Rome explains the proper technique to determine if a patient exhibits any degree of external tibial torsion.Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equ.Ortolani maneuver The most reliable method to check an infant's hips for developmental dysplasia of the hip is the Ortolani maneuver. Tibial torsion is a twisting of the tibia that may originate from intrauterine positioning.
Internal tibial torsion is one cause of intoeing. With internal tibial torsion, the shin bone (tibia) is slightly twisted or rotated, causing the foot to turn in. This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due to internal tibial torsion is generally most noticeable when a child begins walking. The etiology of intoeing (i.e., metatarsus adductus, internal tibial torsion, and increased femoral anteversion) is debated, although the causes generally can be correlated with the patient's age .
In-toeing is a very common reason for children presenting to GPs and orthopaedic clinics. The majority of children are born with 40° of femoral anteversion (in turning of the femurs) and 5 – 10° of internal tibial torsion (in turning of the shin bone). This commonly contributes to the normal clumsiness of toddlers as they learn to walk.
Internal Tibial Torsion (ITT) is a condition in early childhood in which the tibia (leg bone) is twisted inwards axially, causing the child to intoe as he walks. . ITT is universal in infants and toddlers, and when the child takes his first steps, intoeing is the norm. With walking, the ITT resolves, and disappears by 18 to 24 months of age. . Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child's feet to turn inward. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for . usually bilateral in infants. may exhibit positive 'cover-up test' often associated with internal tibial torsion. . Radiographs . views. ensure that patella are facing forwards for evaluation (commonly associated with internal tibial torsion) findings suggestive of Blounts disease. varus focused at proximal tibia. severe deformity. asymmetric .Long-term outlook for tibial torsion. Tibial torsion has a very good prognosis. Many cases correct themselves as the child grows. On rare occasions, tibial torsion can be severe and surgery may be required to straighten the shin bones. Surgery is typically considered after 10 years of age as the torsion is unlikely to change after this age.
tear lab test
web5 de out. de 2022 · 1. Privacy. (Fonte: Privacy/Reprodução) Fonte: Privacy. Um dos principais concorrentes do OnlyFans é a Privacy, uma plataforma nacional para .
tibial torsion test infant|how to measure tibial torsion